
A flat flexible cable ffc helps connect electronic parts easily. It saves space and is simple to use. You often find this cable in laptops, cameras, and phones. It bends well and fits into small spaces. This cable lowers interference and heat. That makes it great for high-performance gadgets. More people want compact and flexible wiring now. This shows how useful and special ffc cables are today.
Key Takeaways
- FFC cables are very thin and can bend easily. This makes them great for connecting parts in small devices like laptops and smartphones. These cables help stop interference and heat. They keep the signal strong for devices that need to work well. FFC cables come in many sizes and pitches. This lets you pick what fits your device best. Picking the right insulation and shielding helps FFC cables last longer. It also helps them work better in different places. FFC cables do not cost a lot and make wiring easier. This is why many people use them in new electronics.
Flat Flexible Cable FFC Basics
What Is an FFC
Flat flexible cable ffc is found in many devices today. This cable is thin and has metal lines side by side. It connects parts inside electronics. The cable bends, so it fits in small places. You see flat flexible cables in devices that need small and strong connections.
Tip: You can find ffc cables in things you use every day. Some examples are:
- Flat-screen TVs
- Game consoles
- Computers
- Cameras
- Cellphones
- Tablets
- Laptops
- Smartphones
Flat flexible cables help save space and make things lighter. They bend more and are easier to put in than round cables. You use ffc cables for fast connections in small gadgets. These cables make building devices quicker and easier.
How FFC Cables Work
Ffc cables move signals and power between electronic parts. The cable has flat metal pieces lined up next to each other. A thin plastic layer covers the metal pieces. This design lets you bend and twist the cable without breaking it. You can put the cable around corners or through tight spots.
Flat flex cables work best for short distances. They give good results in most home electronics. For longer distances, round cables keep signals better. Round cables help stop interference and crosstalk. Flat flexible cables can pick up more noise, especially with fast or heavy data.
You need to check the current and voltage for ffc cables. These numbers depend on how wide and far apart the metal lines are. Here is a table that shows common ratings:
| Trace Width | Current Rating |
|---|---|
| 0.1″ (2.54mm) | Over 2A |
| 1mm pitch | 1.2A |
| 0.5mm pitch | 0.5A |
Pick the cable that fits your device’s needs. Ffc cables give strong connections for many uses. They are easy to put in and bend. You also see ffc in places where saving space and weight is important. Fpc cables look almost the same but use other materials and ways to build them.
FFC Structure and Materials
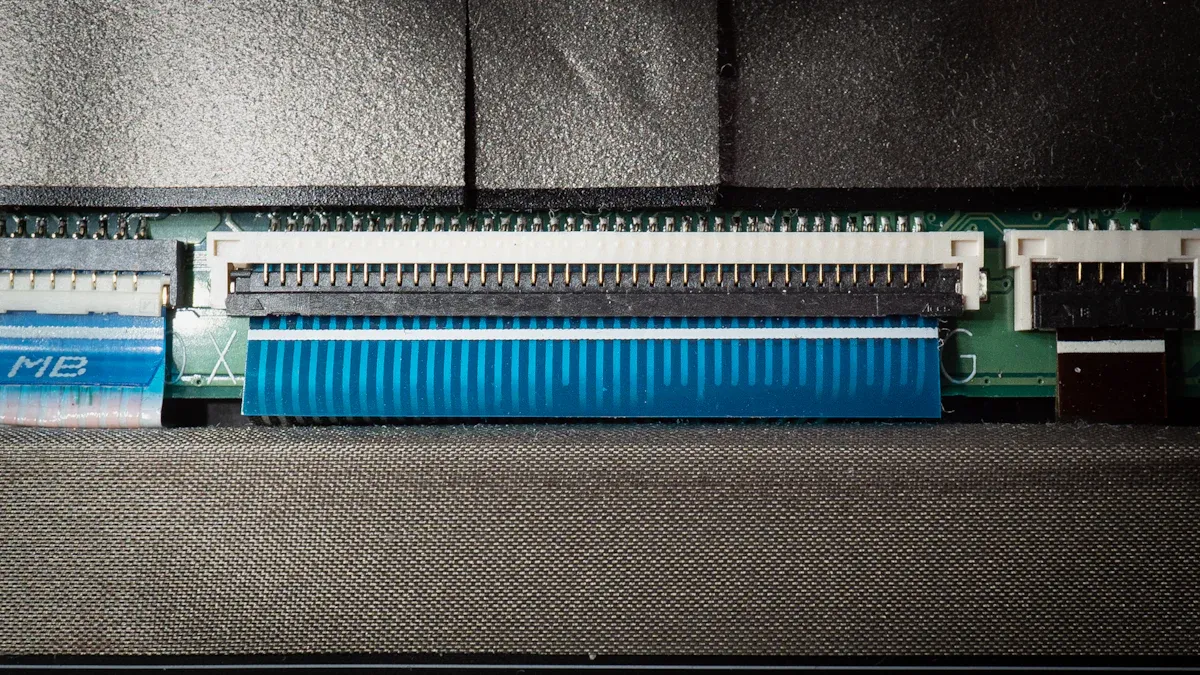
Flat Conductors and Insulation
Inside a flat flexible cable ffc, you see flat metal strips. These strips sit next to each other in a row. This setup lets the cable bend and twist easily. You can fit it into small spaces without losing signal quality. The conductors often use tinned copper. Tin keeps copper safe from rust. This helps the cable last longer. Some cables use copper or aluminum instead.
The insulation covers the metal strips. It uses soft plastic films like polyester or polyimide. These plastics make the cable strong and bendable. Polyester with heat glue sticks well and resists heat. You also find insulation made from PVC, Teflon, or silicone rubber. Each type gives different levels of bending and strength.
Here is a table showing common materials:
| Component | Common Materials |
|---|---|
| Conductors | Copper, Aluminum |
| Insulation | Polyester (PET), Polyimide (PI), PVC, Teflon (PTFE) |
The insulation you pick changes how the cable bends and lasts. PVC bends easily and resists heat and chemicals. Silicone rubber bends well and works in very hot or cold places.
| Insulation Material | Flexibility | Durability | Additional Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | High | Good | Resists heat, chemicals, and moisture |
| XLPE | Moderate | Excellent | Handles heat, strong, low power loss |
| Silicone Rubber | High | Good | Bends very well, works in extreme heat or cold |
| TPE | High | Good | Resists scratches and chemicals, stays strong |
Tip: Tinned copper helps your flat cables stay safe from water and rust. This makes your connections last longer, even in tough places.
Pitch and Shielding
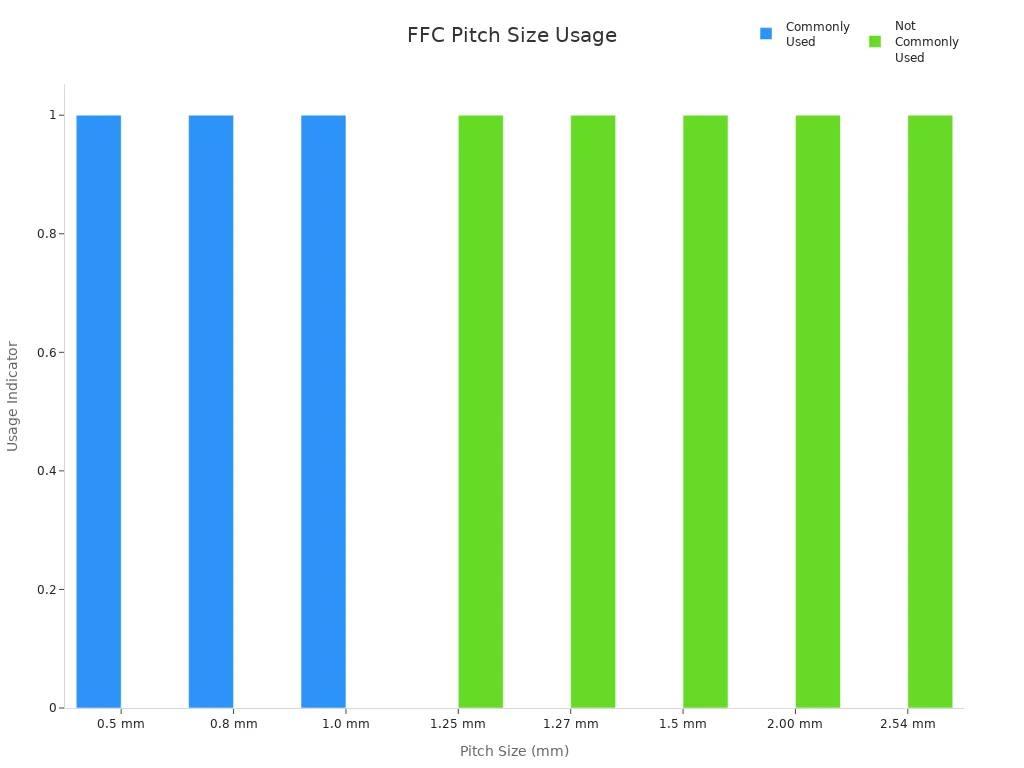
Pitch is the space between each conductor in your cable. You choose the pitch size for your device’s needs. Smaller pitch sizes work best for fast data and tight spaces. Most ffc cables use pitch sizes like 0.5 mm, 0.8 mm, or 1.0 mm. These sizes let you fit more wires in less space.
| Pitch Size (mm) | Commonly Used |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | Yes |
| 0.8 | Yes |
| 1.0 | Yes |
| 1.25 | No |
| 1.27 | No |
| 1.5 | No |
| 2.00 | No |
| 2.54 | No |
Shielding keeps your ffc safe from electric noise. There are different shield types, like braided, foil, spiral, and mixed shields. Foil shields cover the cable fully and work well for fast signals. Braided shields protect well and bend easily. Mixed shields use layers to work better for many signals.
| Shield Type | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Braided shield | Woven metal strands make a bendable mesh | Shields well, 70%-95% coverage. Works against electric and magnetic fields. |
| Foil shield | Thin metal layer stuck to polyester film | Covers fully, great for fast signals. Not as bendable. |
| Spiral shield | Wire wrapped around the cable core | Shields okay, 70%-80% coverage. Works for slow signals. |
| Combination shields | Layers of different shield types | Works best for many signals. Shields electric and magnetic fields well. |
You use ffc, fpc, and flat cables in many fast devices. These cables help keep your connections strong and easy to set up. You get good signal quality in small spaces.
Types and Specifications of FFC Cables
Sizes and Pitches
When picking a flat flexible cable ffc, look at size and pitch. Pitch is the space between each conductor. There are many pitch sizes in electronics. Some pitches are better for small devices. Others fit bigger connectors.
| Pitch (mm) | Common Usage |
|---|---|
| 0.500 | Most common |
| 1.00 | Most common |
| 1.25 | Most common |
| 0.625 | Less common |
| 0.635 | Less common |
| 0.800 | Less common |
| 1.27 | Less common |
| 2.00 | Less common |
| 2.54 | Less common |
You see 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm, and 1.25 mm pitches a lot. These sizes let you fit more wires in small spaces. Smaller pitches are good for fast signals and tight spots. Bigger pitches work for devices with large connectors.
| Pitch Size | Compatibility Impact |
|---|---|
| 0.5mm | Good for small devices |
| 1.0mm | Used in many regular gadgets |
| 0.8mm | Mixes size and performance |
| 1.25mm | For bigger connectors and devices |
The way pins are arranged in ffc cables matters. It affects how signals move and if devices work together. You must match the pin count and layout to your connectors. This keeps your connections strong.
Termination Methods
You can connect ffc cables in different ways. Each way has its own benefits for setup and strength. Here are the main types:
| Termination Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| ZIF style connectors with integral stiffeners | Safe connection, easy to line up |
| Crimp terminated with pins or solder tabs | Works with many housings |
| Direct solder to printed circuit boards | Strong, lasts a long time |
| Discreet wires soldered to ends | Flexible, easy to change |
You might use hot bar soldering, through hole soldering, or connectors. ZIF connectors make setup fast and safe. Crimp connectors fit tightly and keep out water. Soldering gives a strong link for fast signals. Discreet wires let you change your cable for different uses.
When you choose a way to connect, think about cost, speed, and how long it will last. IDC connectors are cheap and quick to put in, but best for straight lines. Crimp connectors keep signals clear and handle shaking well. Pick the method that fits your device and wiring best.
Tip: Pick the right way to connect your cable. This helps your cable work better and makes setup easier.
FFC vs. Other Flat Cables
FFC vs. Ribbon Cables
You may wonder how a flat flexible cable ffc is different from a ribbon cable. Both cables look flat, but they are not the same. Ribbon cables have round wires inside thick plastic. FFC cables use thin, flat metal strips on soft plastic. This makes ffc cables lighter and easier to bend. You can fold and twist ffc cables many times. They do not break easily. Ribbon cables bend a little but do not handle movement well.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Feature / Property | Ribbon Cable | Flex Cable (Flexible Flat Cable) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat wires with thick plastic | Thin conductors on bendable plastic |
| Flexibility | Bends a little, not many times | Bends and folds a lot |
| Durability | Lasts long in still setups | Lasts long in moving setups |
| Conductor Movement | Wires can move and rub | Conductors do not move |
| Signal Quality | Good, but heat can cause issues | Stable, less noise, better signals |
| Heat Dissipation | Can get hot when moved | Lets heat escape better |
| Weight and Size | Heavy and big | Light and small |
| Typical Uses | Computers, printers | Laptops, cameras, folding devices |
| Connector Types | IDC connectors | ZIF, LIF, FFC/FPC connectors |
| Cost | Cheaper for big projects | Costs more to make |
You often see ffc cables in fast devices like laptop screens and keyboards. They fit in tight spaces and bend easily. Ribbon cables work best in places that do not move, like printers or desktop computers.
Note: If you need fast or high-density electronics, ffc ribbon cable works better and gives stronger signals.
FFC vs. FPC
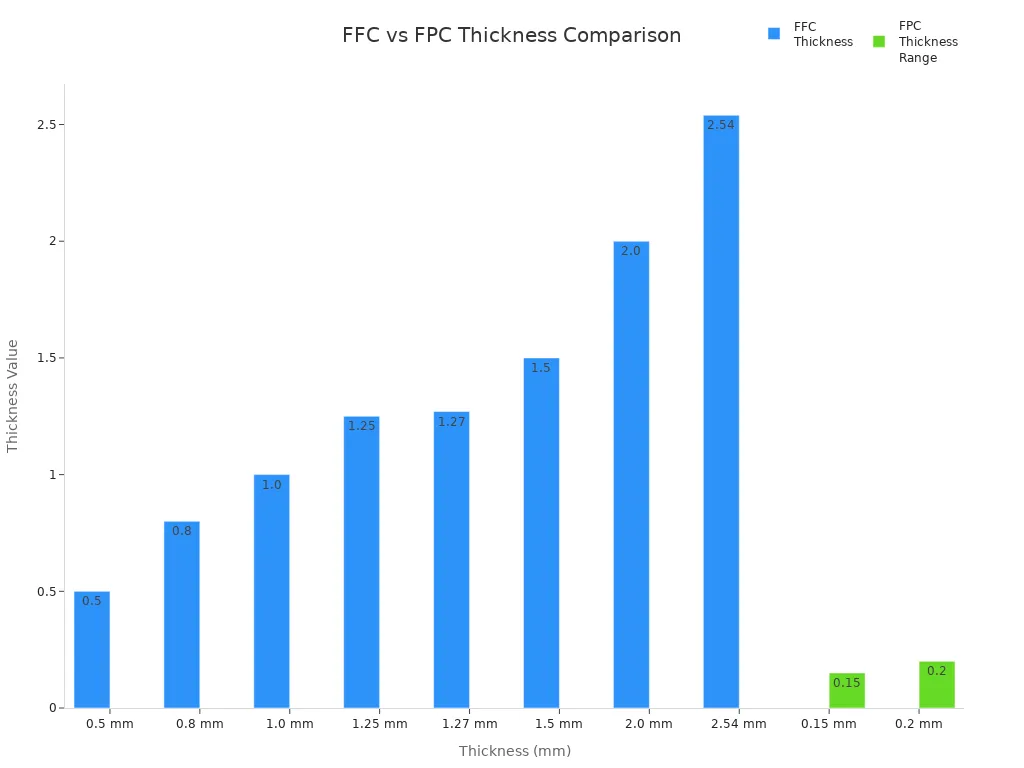
You may also find fpc cables in electronics. The main difference is how they are made and used. FFC cables have flat metal strips on plastic. FPC cables use copper on a printed circuit board. FPC cables are thinner and can be as slim as 0.15 mm. FFC cables start at 0.5 mm thick.
| Type | Thickness Range (mm) |
|---|---|
| FFC | 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.25, 1.27, 1.5, 2.0, 2.54 |
| FPC | 0.15 – 0.2 |
You pick ffc when you want simple and cheap connections for regular layouts. FFC cables are easy to design and install. They work well for crowded electronics where space is tight. FPC cables are better for special shapes and tricky circuits.
| Reason for Choosing FFC | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cost-effectiveness | FFC is cheaper because it is easier to make, especially for lots of cables. |
| Simplicity in design | FFC is good for adding easy, low-cost flat cable links to your device. |
| Suitability for standard layouts | FFC fits regular layouts, so it is great for tight spaces and small budgets. |
Tip: To choose ffc cables, think about what your device needs for bending, speed, and connector type. Custom ffc cables can help you get the best fit for your project.
Flat Flexible Cables Applications

Electronics and Devices
Flat flexible cable ffc is used in many electronics. These cables connect parts inside laptops, tablets, and smartphones. They fit into small spaces and keep devices thin. You also find them in cameras, printers, and game consoles. Flat flex cables link screens, keyboards, and batteries. Ffc cables move high-speed data in advanced systems. They work well in devices needing fast signals and strong control.
Here are some ways ffc cables are used:
- Laptops and tablets use them for screens and keyboards.
- Smartphones use them for batteries and cameras.
- Printers and scanners use them for moving parts.
- Game consoles use them for fast and steady links.
- Medical devices use them for small size and high power.
The thin and bendable shape helps make smaller gadgets. You get better signal control and easy wiring in tight spaces. These cables also support fast and high-frequency signals, which boost how well things work.
Flexible Flat Cable Assemblies Benefits
Flexible flat cable assemblies have many good points. They save space because they are not thick like round cables. They bend and fold easily without breaking. Being light helps make portable devices use less energy. They let heat out, so your device stays cool and works well.
| Benefit of Flexible Flat Cable | Description |
|---|---|
| Slim Profile | Fits in small spaces, not bulky |
| Enhanced Flexibility | Bends well, good for moving parts |
| Lightweight Performance | Makes devices lighter, saves energy |
| Improved Thermal Management | Lets heat out, keeps things cool |
| Customizable Configurations | Can be made for special systems |
Flexible flat cable assemblies also cost less to make. They make wiring simple and lower the chance of problems. You can build devices faster because there are fewer steps. These assemblies come with connectors and other needed parts. This gives you a ready-to-use system. You keep things the same and strong in every product, which matters for advanced systems and flexible circuits.
Tip: If you pick flexible flat cable assemblies, you get better performance, easy wiring, and strong links for your electronics.
Flat flexible cable ffc is a good pick for new electronics. These cables help save space inside your device. They last a long time and keep signals strong, even when fast. New designs for insulation and conductors make them work better. This also makes ffc cables easier to use. When you choose ffc or fpc, look at what they are made of. Check if they have shielding and if they fit your environment. The table below shows the main benefits:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Space-saving design | Efficient use of device space |
| Flexibility | Bends in tight areas |
| Improved signal integrity | Reduces interference |
| High durability | Extends device lifespan |
- Try ffc cables if you need small and bendy wires for your project.
- Look at how you will route the cable, what shielding you need, and what materials work best.
FAQ
What does FFC stand for?
FFC stands for flat flexible cable. You use it to connect parts inside electronic devices. It is thin, flat, and bends easily.
Can you cut or trim an FFC cable?
You should not cut or trim an FFC cable. Doing this can damage the cable and stop it from working. Always use the correct length for your project.
How do you connect an FFC cable to a device?
You connect an FFC cable by sliding it into a special connector. This connector holds the cable in place. Make sure you line up the cable with the connector pins.
Where do you find FFC cables in electronics?
You find FFC cables in laptops, printers, cameras, and game consoles. They connect screens, keyboards, and other small parts inside these devices.
