When comparing FFC vs FPC cable, you’ll notice key differences. FFC cables feature flat wires that make connections simple and straightforward. On the other hand, FPC cables are designed to handle more complex circuits and are ideal for tight spaces and challenging environments. Understanding the distinctions between FFC vs FPC cable helps you select the best option for your specific needs.
| Feature | FFC | FPC |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Very High |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Simple | Complex |
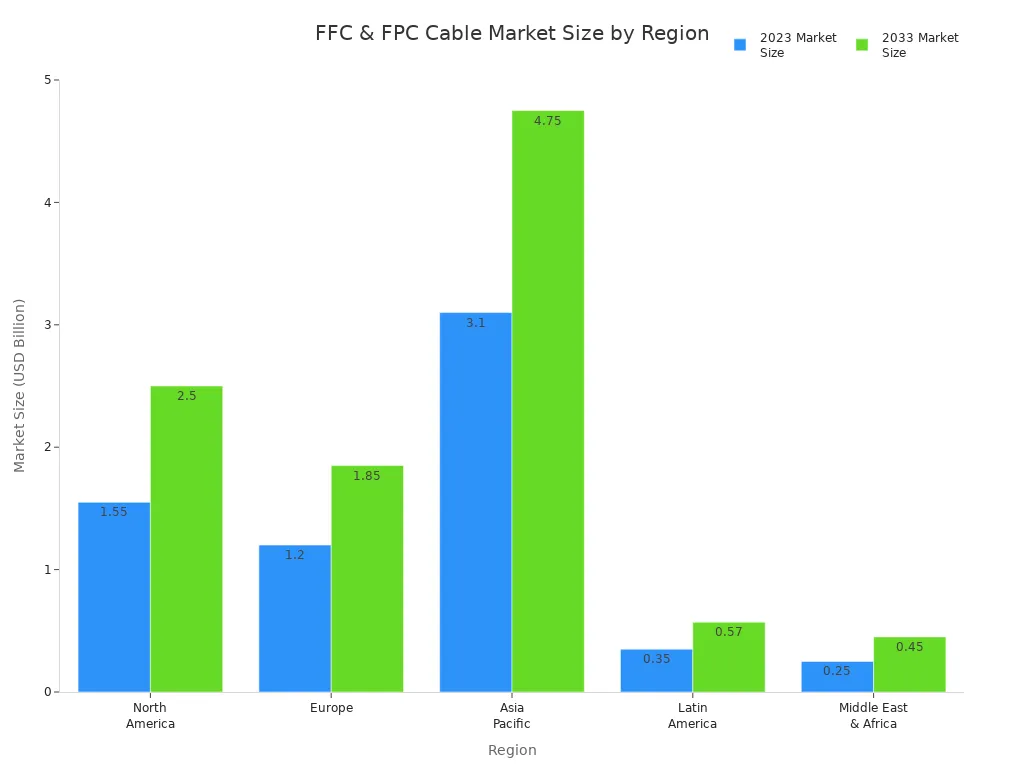
Both FFC and FPC cables are seeing growth in the market, especially in electronics and automotive industries. Knowing how FFC vs FPC cable are constructed and their durability will help you make a more informed choice.
Key Takeaways
- FFC cables are simple and cheap. They bend easily. They work well in things like laptops and printers that move.
- FPC cables are thinner and last longer. They can handle harder jobs. They fit in small spaces and work in advanced things like medical tools and foldable phones.
- Use FFC if you need easy, straight wires or if the cable will bend a lot. Use FPC if you need many layers or tight spaces, or if the place is rough.
- Using the right connector with your cable helps it work better and last longer.
- Think about cost, how much it bends, and how strong it is. This helps you pick the best cable for your project and stops problems.
FFC vs FPC Cable Overview
Flexible Flat Cable (FFC)
Flexible flat cable is found in laptops, printers, and cameras. FFC uses flat wires spaced apart on plastic film. This makes the cable easy to bend in small spaces. Manufacturers make FFC by putting copper wires between PET or PEN layers. The process is simple and saves money. You get one layer of wires, which works well for basic power and signals.
Here is a quick comparison of FFC features:
| Feature | Flexible Flat Cable (FFC) |
|---|---|
| Design | Flat wires on plastic film |
| Flexibility | High, good for simple bends |
| Application | Used in electronics, laptops, printers |
| Cost | Lower because of simple design |
| Thickness | Thin, just a few millimeters |
| Connector Options | Pre-made or bare for soldering |
New lamination technology makes FFC ribbon cable stronger and more reliable. Automated assembly helps keep costs low and quality high. Flat flexible cables help make electronics smaller, saving space but keeping good performance.
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC)
Flexible printed circuit cables bend more and are thinner than FFC. You find FPC in medical devices, aerospace parts, and advanced electronics. Manufacturers use polyimide and etch copper wires onto it. This lets them make many layers and complex circuits.
FPC can fold, twist, and fit into tiny spaces. You can use FPC for high-density and high-performance jobs. Making FPC needs copper coating, etching, and stacking layers. These steps make FPC cost more but also last longer and work better.
Here is a table comparing FPC features:
| Feature | Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) |
|---|---|
| Design | Wires printed on flexible polyimide |
| Flexibility | Very high, bends and folds often |
| Application | Used in medical, aerospace, hearing aids, solar cells |
| Cost | Higher because making it is harder |
| Thickness | Can be as thin as 0.3mm, comes in many layers |
| Connector Options | Built into circuit assemblies |
Flexible printed circuit technology helps new ideas in electronics. FPC and FFC cables both give strong electrical connections, even when bent or twisted. As electronics get smaller, more industries need these cables.
Construction
Materials
When you compare the materials in flexible flat cable and flexible printed circuit, you see they are different. FFC cables use copper or aluminum as flat conductors. Most FFC cables use copper, which is strong and flexible. In 2023, copper made up more than 60% of the market. The conductors are placed between polyester or polyimide film layers. Polyester is cheap and light, so it is used a lot. Polyimide is better for heat and does not soak up water easily. If you need a cable for hot or wet places, polyimide is the best choice. Polyester can take in water, which can make it swell and weaken the cable.
FPC cables also use polyimide and polyester films as their base. Polyimide is the top choice for flexible printed circuit designs. It is strong, handles heat, and works well with electricity. This makes FPC good for devices that bend, fold, or get hot. Polyester film is lighter and keeps the cable thin, but it is not as tough as polyimide. Good connectors use high-quality metals to make sure the cable works well.
Tip: Polyimide-based FPC cables are best for small, high-tech electronics that need to last a long time.
Structure
The way FFC and FPC cables are built changes how you use them. FFC cables have flat copper wires between thin polyester or polyimide layers. This makes them light and easy to bend. You can bend them in one direction, which is good for folding or sliding parts. Some FFC cables have special shapes, stiff parts, or extra layers to make them stronger. The flat shape lets the wires be close together, so the cable stays small.
FPC cables have a more detailed structure. They have copper layers with polyimide, and you can pick single, double, or many layers. The copper is shaped into special patterns, so you can make complex circuits in a small space. FPC cables are thinner than FFC cables, usually only 0.15mm to 0.3mm thick. Because they are thin and bendy, you can use them in tight spaces where other cables will not fit.
| Feature | FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) | FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Configuration | Copper layers with polyimide; single, double, or multilayer | Flat copper wires between polyester layers |
| Conductor Layout | Chemically etched custom patterns | Parallel flat wires with fixed spacing |
| Thickness | 0.15mm to 0.3mm (very thin) | 0.5mm to 2.54mm (thicker) |
| Flexibility | Very high, supports 3D shapes | High, best for one-direction bends |
You should pick the cable structure that fits your project. FFC is good for simple, flat connections. FPC is better for tricky, crowded, or bendy designs.
Features
Flexibility
You should think about flexibility when picking between ffc and fpc. Ffc cables bend many times without breaking. Their flat metal wires and plastic film help them bend easily. You can use them in places where the cable moves a lot. Printers and laptops often use ffc because the cable bends every time you open or close the device.
Fpc cables are better for spots that do not move much. Most flexible printed circuit designs need a bend radius of 5-6 mm. If you bend them too sharply or too often, they might break. Some special fpc cables use copper that does not crack easily, but these are rare. It is best to bend fpc gently and not too many times so it lasts longer.
Tip: Pick ffc for moving parts and fpc for tight, fixed spaces.
Durability
Durability is important if you want your project to last. FFC cables are strong enough for daily use. They can handle lots of bending and movement. This makes them good for things that open and close a lot.
Fpc cables are very tough in small or harsh places, especially if you do not move them much. The polyimide in flexible printed circuit designs stands up to heat and chemicals. If you need a cable that stays still but faces tough conditions, fpc is a great choice.
Thickness
Thickness matters when you need to fit cables in small spaces. Ffc cables are thin, but fpc cables are even thinner. Some fpc connectors, like the Hirose Electric FH82, are only 0.2 mm thick. This super-thin design helps save space in small electronics like smartphones or medical devices.
| Product / Series | Thickness (mm) | Application / Suitability Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hirose Electric FH82 FPC Connector | 0.2 | Great for places with little space |
| TE Connectivity Ultra Low-Profile FPC | Ultra-thin | Made for small electronic assemblies |
These thin cables and connectors help make devices smaller and lighter. The right thickness lets you add more features in less space.
FFC vs FPC: Key Differences
Wiring and Routing
FFC and FPC cables are not the same. FFC cables have flat copper wires next to each other. This makes electricity move in a straight line. You can see where the cable goes, so it is easy to put in. FFC is good when you need a simple path.
FPC cables are like tiny circuit boards. They can have many layers and twisty paths. This helps fit more wires in small places. FPC bends, folds, and twists to fit tight spots. You can put electronic parts right on the cable. FPC is great for advanced gadgets.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Feature | FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) | FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure & Function | Flat cable with simple 1:1 linear wiring | Flexible mini circuit board with complex routing |
| Customization | Standardized, reusable | Custom-designed for specific tasks |
| Design Complexity | Linear routing only | Supports multi-layer, angled, impedance-controlled paths |
| Cost & Reusability | Lower cost, reusable | Higher cost, limited reusability |
| Flexibility & Durability | Good for repeat-use connections | Better in tight spaces, harsh environments |
Tip: Pick FFC for simple, straight wiring. Choose FPC if you need lots of wires in a small or odd space.
Connector Types
FFC and FPC use different connectors. FFC connectors work with flat, ribbon cables. They have open metal ends and simple locks. You can put them in fast. They are good for things you open and close a lot.
FPC connectors are more complex. They use metal pads, holes, and sometimes pressure contacts. You must line them up carefully. FPC connectors bend more and last longer, even in tough places. Some connectors work with both FFC and FPC, but you need to match the size and number of circuits.
Here is a table to compare FFC and FPC connectors:
| Parameter | FFC Connectors | FPC Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Designed For | Flat flex cables | Flexible PCB tail sections |
| Termination | Exposed conductors | Plated pads and through-holes |
| Pitch (spacing) | 0.3mm to 1.27mm | 0.2mm to 1.5mm |
| Current | < 1A typical | Up to 5A depending on pins |
| Actuation Method | Latch, clasp, slide lock | ZIF, pressure actuated contacts |
| Durability | ~10,000+ mating cycles | ~100,000+ mating cycles |
| Resistance | ~100+ milliohms | < 50 milliohms |
| Contact Type | Pads or pins | Pins with wiping contacts |
| Alignment | Self-aligning housing | Positive positioning guides |
Always pick the right connector before you pick your cable. This stops problems and makes your system work better. Brands like Molex, Hirose, and KYOCERA AVX have many connector choices. Matching the connector and cable makes your project safer.
Cost
Cost matters when you choose FFC or FPC. FFC cables cost less because they use simple stuff and easy steps. You get plastic film with metal wires on one side. This keeps the price low. FFC is good for basic jobs.
FPC cables cost more. They use special polyimide that can be ten times pricier than FFC materials. Making FPC needs more steps, like etching, drilling, and stacking layers. You need better machines and controls. These things make FPC more expensive. FPC is worth it when you need thin, bendy, and complex cables.
- FFC cables are best for simple, cheap projects.
- FPC cables are better for advanced, crowded, or tiny designs, even if they cost more.
Note: Pick FFC if you want a basic, low-cost cable. Pick FPC if you need a cable for tight spaces or lots of connections, even if it costs more.
Applications of FFC and FPC
Consumer Electronics
You can find ffc and fpc in many electronics. These cables help make gadgets smaller and lighter. Ffc cables are used in phones, tablets, laptops, and screens. Their flat shape saves space inside the device. You can bend or fold them, and they will not break. This is good for things like laptops and cameras that open and close.
Here are some reasons ffc cables are a good choice:
- Their flat shape fits into small spaces.
- You can bend or fold them many times.
- They move data quickly and work well.
- They cost less than other cables.
Fpc cables are used in even more advanced devices. You see them in foldable phones, smartwatches, and other new gadgets. Fpc cables are thinner and can twist or fold in tricky ways. They can also hold tiny parts like LEDs or chips. This helps make devices smaller and smarter.
| Device Type | FFC Use Example | FPC Use Example |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphone | Battery and screen connectors | Foldable screens, camera modules |
| Laptop | Keyboard and touchpad links | Hinges, flexible circuit boards |
| Wearable | Simple display connections | Heart rate sensors, curved displays |
| Printer/Scanner | Moving parts, print heads | High-density control circuits |
Tip: Use ffc for simple, straight connections. Pick fpc if you need to fit circuits in tiny or odd spaces.
Automotive and Industrial
Cars and factories need strong cables for hard jobs. Ffc cables connect GPS, radios, and dashboard screens. Their flat shape lets you hide them behind panels. In electric cars, ffc cables link batteries and sensors. This helps keep the car safe and working well.
Fpc cables are great where things move or shake a lot. You find them in steering wheels, engine sensors, and door controls. Fpc cables bend and twist many times and do not break. They also stand up to heat, shaking, and chemicals. This is important in cars and factories.
- Ffc cables are good for:
- Connecting screens and controls in dashboards
- Linking sensors in electric cars
- Helping machines watch and check things in real time
- Fpc cables are best for:
- Engine wires and transmission sensors
- Robots and machines that move all the time
- Control panels and moving belts in factories
| Parameter | FFC Cables | FPC Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Very high |
| Vibration Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | Up to 120°C | -40°C to 120°C (or higher) |
| Typical Use | Displays, sensors, infotainment | Engine, robotics, ADAS, moving mechanisms |
Note: For places with lots of movement or tough conditions, fpc cables last longer and work better. Use ffc cables for easier, less stressful jobs.
Medical Devices
Medical tools need cables that are safe and easy to clean. Ffc cables are used in monitors, scanners, and other medical machines. The cable must be safe for people and able to be cleaned many times. Ffc cables made from special plastics and metals are good for this. They stay flexible and strong after cleaning.
If you need to make very small devices, fpc cables are the best. Fpc cables help build tiny medical tools like hearing aids and endoscopes. Their thin, bendy shape fits into very small spaces. Fpc cables also use fewer connectors, so they break less and work better.
| Consideration | FFC Cables | FPC Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Medical-grade plastics and metals | Polyimide and thin copper, safe for patients |
| Sterilization | Withstands gamma, ETO, autoclave | Handles repeated sterilization |
| Miniaturization | Good for small devices | Excellent for ultra-compact tools |
| Reliability | Flexible, durable, easy to connect | Fewer connectors, high reliability |
- Ffc cables are best for:
- Patient monitors and imaging machines
- Devices that need to be cleaned and sterilized often
- Fpc cables are best for:
- Hearing aids, endoscopes, and devices inside the body
- Jobs where space is tiny and the cable must not fail
Remember: Always make sure your cable is safe and can be cleaned before using it in any medical tool.
Common Concerns
Shielding
Shielding keeps cables safe from electromagnetic interference. This is important in places with lots of noise or high-frequency signals. You can pick different shielding types, and each one helps in its own way.
| Shielding Option | Construction Details | Application Method | EMI Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foil Laminated Shield | Uses aluminum foil with a polyester layer | Put on one or both sides; connect with drain wires or IDC pins | Cuts down EMI; works best for cable pitches like 1.27mm or 2.54mm |
| Silver Loaded Epoxy Shield | Has silver epoxy covered by PET film or special coating | Sprayed on; can cover certain spots; connects through small openings | Gives full shielding; lowers noise, cross talk, and signal loss |
| Grounding Options | Holes in the outside let you ground to the chassis | Use drain wires or connect straight to the chassis | Makes EMI shielding better by giving a low resistance path to ground |
Shielding does more than block EMI and cross talk. It helps cables last longer in tough places. Shielding keeps signals strong and protects from dust, water, and chemicals.
Standards
Industry standards help you choose the right cable. In cars and planes, rules like AS9100 and IATF 16949 are very strict. These rules make sure cables work well in heat, shaking, and wet places. They also make sure you can track and trust your cables so they do not fail.
| Standard Category | FFC Cable Standard | FPC Cable Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Flex Cycle Testing | IPC-TM-650 2.4.3 | IPC-TM-650 2.4.3.1 |
| Impedance Control | Not used | IPC-2141A |
| Material Certification | UL 94V-0 | IPC-4101/102 Slash Sheets |
If you pick cables with these standards, you get better safety, strength, and performance. Always look for these certifications if your project must be very reliable.
Extension Options
There are many ways to make FFC and FPC cables longer. You can use FFC/FPC connectors, FFV connectors for vertical use, or FPC mezzanine connectors for stacked cables. Board-to-board connectors and crimp or solder ends also help you join cables.
- Flat cable sets with built-in connectors are easy to use for extensions.
- You should use strain relief and make ends stronger so cables do not break.
- Protect cables from rubbing and follow bend rules so they do not snap.
- ZIF connectors let you put in and take out cables easily, but you must line them up and check thickness.
Good design and careful setup keep cable extensions working well. In hard places, you might need extra shielding or support so cables do not fail.
Picking FFC or FPC cables depends on what your project needs. FFC cables are good for easy jobs and save money. FPC cables are better for hard circuits and rough places. Look at the table below to see the main differences:
| Factor | FFC Cable | FPC Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | High | Very High |
| Circuit Complexity | Simple | Complex |
If your project is tricky or in a tough spot, ask an expert or check guides like the Electronic Connector Book to help you pick the right cable.
FAQ
What is the main difference between FFC and FPC cables?
FFC cables use flat, parallel wires inside a plastic film. FPC cables use printed circuits on a flexible board. You choose FFC for simple connections. You pick FPC for complex, tight spaces.
Can you reuse FFC and FPC cables?
You can reuse FFC cables many times. They work well for devices you open and close often. FPC cables are less reusable. They fit best in fixed, permanent setups.
Are FFC and FPC cables safe for high temperatures?
FPC cables handle high heat better than FFC cables. Polyimide in FPC resists temperatures up to 200°C. FFC cables with polyester work up to 105°C. Always check your cable’s material before use.
How do you choose the right connector for these cables?
Always match the cable type, pitch, and thickness with the connector. FFC connectors use exposed metal ends. FPC connectors use pads or holes. Check the datasheet for compatibility.
Can you cut or customize FFC and FPC cables?
You can cut FFC cables to length with scissors. FPC cables need special tools for cutting and shaping. Customizing FPC cables often requires help from a manufacturer.

