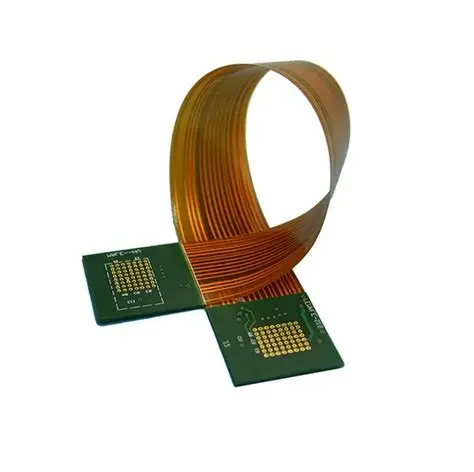

A flexible PCB board, also called a flex PCB, uses bendy materials. These materials help make circuits that fit in small spaces. Rigid PCBs cannot bend, but flex PCBs can. Engineers can shape flex PCBs around curves or folds in devices. Flexible printed circuit boards give strong connections in tricky layouts. Flex PCBs work in wearable electronics, medical devices, and cars. Their flexibility and strength help in devices that move a lot. > Flex circuit boards can handle shaking and heat. This makes them useful for many things. Flexible PCBs and flex PCBs help with new devices. They give engineers more ways to design.
Key Takeaways
- Flexible PCBs can bend and twist to fit tight spaces. This helps make devices smaller and lighter. They use tough materials like polyimide and copper. These materials help them last and work well with heat and movement. Flexible circuit boards help device design by saving space. They also make devices lighter and handle heat better. These boards are used in phones, wearables, cars, and medical devices. They last longer and work well for a long time. Flexible PCBs cost more and need careful handling. But their design helps engineers make better and smaller products.
Flexible PCB Board Overview
What Is a Flexible PCB Board
A flexible pcb board is made from thin, bendy stuff. This lets it make circuits that can fit in small or weird spaces. Engineers use these boards when devices need to be tiny or shaped oddly. Polyimide is the main material in a flex pcb. It does not melt easily and lets the board bend without snapping. Copper is used for the lines that carry electricity. The flexible pcb board can twist, fold, or wrap around other parts. This helps people design smaller and lighter things.
Tip: Flex pcb boards are good for things that move or shake, like fitness trackers and medical sensors.
A flex pcb can have one, two, or many layers. More layers give more room for circuits and wires. The board stays thin even with extra layers. This helps it fit in small electronics.
Flex PCB vs Rigid PCB
Flex pcb and rigid PCB are not the same. The table below shows how they are different:
| Feature | Flex PCB | Rigid PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyimide, flexible | FR4, hard epoxy |
| Shape | Bendable, foldable | Fixed, flat |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Durability | Handles bending | Breaks under stress |
| Applications | Wearables, medical | Computers, TVs |
A flex pcb can bend and twist to fit in curved or moving things. Rigid PCBs stay flat and cannot bend. Flex pcb boards are lighter and save space. Rigid PCBs are strong and hold big parts. Engineers pick a flex pcb when they need it to bend and last a long time.
Features of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
Materials and Construction
Flexible printed circuit boards use special materials for their features. Polyimide substrates make up most flexible circuits. Polyimide does not melt and is hard to break. Acrylic-based adhesives stick the layers together. These adhesives keep the circuits strong when bent. Copper traces make paths for electricity on flexible pcbs. Each layer is thin and smooth, so circuits can be packed tightly. Even thickness helps flexible circuits fit in small spaces. Engineers pick these materials for modern electronics because they work well.
Note: Polyimide and acrylic-based materials make flexible circuits strong and bendy.
Mechanical Properties
Flexible pcbs have great mechanical features. They can bend a lot without breaking. Flexible circuits can twist, fold, or wrap around parts. Flex circuits do not break from shaking or bumps. They work in hot and cold places. Flex pcbs can bend many times and still work. These features make flexible printed circuit boards good for devices that move or change shape.
Types of Flexible PCBs
There are different types of flexible circuits. Single-sided flex circuits have one copper layer. Double-sided flex circuits have two layers for harder designs. Multi-layer flex circuits stack layers for more paths. Rigid-flex pcbs mix flexible and stiff parts for support and bending. Thermoformed flex pcbs keep a 3D shape after heating. These types help engineers make products that bend and fit many shapes. Flex circuits and flex pcbs help save space and lower weight in devices.
Tip: Pick the right flexible circuit type for your device and its needs.
Advantages of Flexible Circuit Boards
Space and Weight Reduction
Flexible circuit boards help make products smaller and lighter. These boards are thin, so they use less space inside devices. They can bend and fold to fit into tight or odd spots. This helps modern electronics become smaller and lighter. Many companies use flexible circuit boards in phones, tablets, and wearables. These gadgets need to be light and easy to carry. Flexible circuits also remove the need for big wires and connectors. This makes products more compact and efficient.
Tip: Flexible circuit boards let designers make slim gadgets you can carry in your pocket or wear on your wrist.
Electrical Integrity
Flexible circuits give strong electrical performance. They keep connections steady, even when the device bends or moves. This is a big benefit of flexible printed circuit boards. Flexible circuit boards use tough materials that do not crack or break easily. The copper lines stay in place, so signals move without stopping. Flex circuit boards work well in things that bend a lot, like folding phones or medical sensors. These boards also lower the chance of loose wires or broken connections. Flexible circuits help devices last longer and have fewer problems.
Heat Dissipation
Flexible circuit boards handle heat better than many other circuits. The thin layers let heat move away from important parts. This keeps sensitive electronics safe from damage. Flexible circuits also work well in harsh places, like high heat or strong shaking. Many engineers use flexible circuit boards in cars, planes, and machines. These places need circuits that can survive tough conditions. Flex pcbs help cool devices and make them last longer.
Note: Good heat dissipation means flexible circuit boards can work where other boards might not.
Design Flexibility
Flexible circuit boards give engineers more ways to design. They can twist, fold, or wrap around other parts. This helps make new shapes and uses for products. Flexible circuits can connect moving parts, like hinges or arms that turn. Flex pcbs make assembly easier and need fewer parts. Flexible circuits also let engineers build things that were not possible before. The advantages of flexible circuit boards make them great for creative projects.
- Flexible circuits can be used in 3D layouts.
- They cut down on the number of connectors needed.
- Flexible circuit boards help save time when putting things together.
The benefits of flexible printed circuit boards are more than just saving space. Flexible circuits help engineers fix hard design problems. Using flexible circuit boards gives better performance, longer life, and more choices for new products.
Limitations of Flexible PCBs
Mechanical Constraints
Flexible PCBs can bend and twist, but not everywhere. If you bend one spot too much, the copper can crack. Sharp folds might break the circuit. Flex PCBs are not good for heavy parts. Rigid boards hold big chips better. You must handle flex circuits gently when building things. Pulling or stretching can hurt the thin layers. Devices that move a lot can wear out the flex PCB. Designers need to think about these limits to keep things working.
Note: Flex PCBs work best if you do not bend them sharply or put heavy parts on the flexible area.
Cost Factors
Some things make flexible PCBs cost more than rigid ones. The material you pick matters a lot. Polyimide is more expensive than FR-4. Adhesiveless cores work better but cost more. More layers can make a flex PCB up to 40% pricier. Big or odd-shaped boards waste material and cost more. Thin traces and close spaces need special tools, which adds cost. Thick copper and tiny drill holes also raise the price. Surface finishes like ENIG last longer but cost more. Stiffeners made from metal or special plastics add to the price. Using panels well and fewer vias can help save money.
- Material type (polyimide, adhesiveless cores)
- Number of layers
- Board size and shape
- Trace width and spacing
- Copper thickness
- Drill hole size and clearance
- Surface finish (ENIG, silver, tin)
- Stiffener type (FR4, polyimide, metal)
Designers have to balance what they want and what they can spend when picking flex PCBs.
Manufacturing Challenges
Making flexible PCBs is harder than making rigid ones. The thin stuff can wrinkle or tear while being made. Putting and soldering parts on a flex board needs extra care. Machines must be gentle so the boards do not get hurt. Lining up many layers takes skill and good tools. Checks must find small cracks or weak spots. Some shapes or sizes are tough to make with flex circuits. These problems can slow down making the boards and cause waste. Factories need trained workers and special tools to make good flexible PCBs.
Tip: Careful design and skilled workers help stop problems with flexible PCBs.
Applications of Flex PCB
Flexible circuits are important in many new devices. Flex pcbs are used in lots of different industries. Engineers use flexible circuits to fix design problems. They also help devices work better. The next parts show how flexible circuits are used in electronics, cars, and medical tools.
Consumer Electronics
Flexible circuits help make small and strong gadgets. Phones, tablets, and laptops use flexible circuits to link screens, batteries, and cameras. These circuits fit in tiny spaces. They help keep devices thin and light. Smartwatches and fitness trackers also use flexible circuits. These gadgets need to bend and move with people. Flexible circuits help make foldable phones and other cool new gadgets.
- Flexible circuits link moving parts in folding screens.
- They cut down on big wires in gadgets.
- Flexible circuits help portable electronics last longer.
Tip: Flexible circuits make gadgets lighter and easier to use.
Automotive Uses
Cars and trucks need flexible circuits that work well. Flexible circuits are used in dashboards, sensors, and lights. Flex-to-rigid PCBs mix flexible and stiff parts for support. Polyimide can handle heat, water, and chemicals. Rolled annealed copper foil lets circuits bend without breaking. Special coatings protect circuits from tough car conditions.
- Flexible circuits can handle shaking, heat, and wetness in cars.
- Engineers use the right bend shapes to stop cracks.
- Hot parts go on stiff areas to cool better.
- Careful tests make sure flexible circuits last a long time.
Flexible circuits help car parts work safely, even when things get rough.
Medical Devices
Flexible circuits help make small medical tools. They fit in tiny or odd-shaped spaces. This is good for health wearables, implants, and test tools. Their light weight makes them easy for patients to wear. Flexible circuits make wiring simple and save space. New ideas like 3D flexible circuits help medical tools fit the body and move with people.
- Flexible circuits help make tiny medical devices.
- They make devices more comfy and work better.
- Better sensors help new medical tools do more.
Note: Flexible circuits meet health rules and help medical tools work better.
Engineers keep finding new ways to use flexible circuits. Flexible circuits help make new things in electronics, cars, and health care.
Flexible PCB boards have lots of good points. They take up less space and weigh less. They also deal with heat really well. Engineers use them to build strong and dependable things in many fields. Flexible PCBs help things last longer and work better.
If you know how flexible PCBs work, you can choose the right one for your project. Good choices make products better and stop problems from happening.
- Flexible PCBs help bring new ideas to electronics.
- They let people make gadgets that are smaller, lighter, and tougher.
FAQ
What makes flexible PCBs different from rigid PCBs?
Flexible PCBs can bend and twist easily. Rigid PCBs always stay flat. Flexible PCBs use polyimide, which does not melt. Rigid PCBs use hard epoxy that cannot bend. Flexible PCBs fit into small or curved places. Rigid PCBs work best in flat devices.
Can flexible PCBs handle high temperatures?
Flexible PCBs use polyimide that can take high heat. They work well in hot places like cars and machines. Polyimide does not melt when it gets hot. Flexible PCBs keep working even when it gets hotter or cooler.
Tip: Polyimide helps flexible PCBs last in heat and tough spots.
Where do engineers use flexible PCBs most often?
Engineers use flexible PCBs in phones, wearables, cars, and medical devices. These boards fit into tight spaces and move with the device. Flexible PCBs help make gadgets smaller and lighter.
| Industry | Common Use |
|---|---|
| Consumer Tech | Phones, watches |
| Automotive | Sensors, lights |
| Medical | Implants, monitors |
Are flexible PCBs more expensive than rigid PCBs?
Flexible PCBs usually cost more than rigid PCBs. Polyimide and special glue make them pricier. Making flexible PCBs needs careful work and special tools. Designers must think about cost and benefits before picking flexible PCBs.
